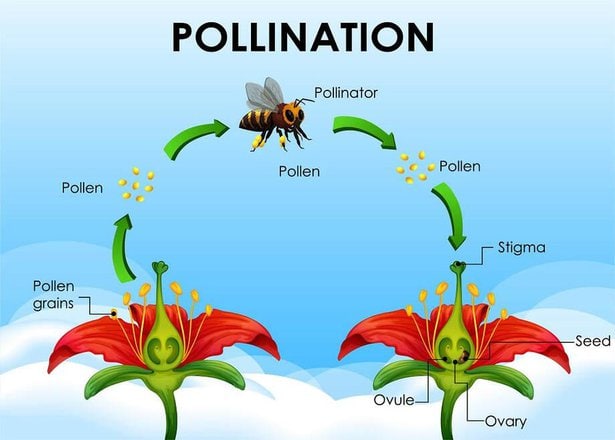
Pollination plays a crucial role in fruit production in gardens, ensuring the successful reproduction of plants and the development of healthy, abundant fruits. This natural process involves the transfer of pollen grains from the male reproductive organs to the female reproductive organs of plants, leading to fertilization and the production of seeds.
Pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, birds, and bats, play a vital role in facilitating this process by transferring pollen from one flower to another. There are different types of pollination, including self-pollination and cross-pollination, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The benefits of pollination extend beyond fruit production, as it also promotes genetic diversity, enhances plant resilience, and supports ecosystem stability. However, several factors, such as habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change, can negatively impact pollination.
To ensure successful pollination in your garden, attracting pollinators and implementing hand pollination techniques can be beneficial. Additionally, certain tips, like proper plant selection and maintenance, can help maximize fruit production in your garden.
The Process of Pollination
The process of pollination is a crucial step in the reproductive cycle of plants, as it facilitates the transfer of pollen from the male reproductive organs to the female reproductive organs, leading to fruit production in your garden.
Pollination can occur through various mechanisms, including wind, water, and most commonly, through the assistance of pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds.
When a pollinator visits a flower, it inadvertently brushes against the reproductive organs, picking up pollen grains in the process. These pollen grains are then transported to another flower, where they are deposited onto the stigma, the female reproductive organ.
This transfer of pollen allows for fertilization to occur, leading to the development of seeds and ultimately, the formation of fruits.
Without pollination, fruit production would be greatly limited, resulting in a scarcity of fresh produce in your garden.
The Role of Pollinators
One cannot underestimate the significance of pollinators in ensuring successful reproduction and the survival of various plant species. Pollinators play a crucial role in the process of pollination by transferring pollen from the male reproductive organs (anthers) to the female reproductive organs (stigma) of flowers. This transfer of pollen allows for fertilization to occur, leading to the development of fruits and seeds. Pollinators include a wide range of organisms such as bees, butterflies, moths, birds, bats, and even some mammals. They are attracted to flowers by their colors, scents, and nectar, and inadvertently carry pollen as they move from flower to flower in search of food. Without pollinators, many plants would not be able to reproduce, resulting in a significant decline in fruit production and biodiversity.
Types of Pollination
Types of pollination vary among different plant species and involve a range of pollinators such as bees, butterflies, birds, and bats. There are two main types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Self-pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from the male reproductive organ (anther) to the female reproductive organ (stigma) within the same flower or on the same plant. This type of pollination ensures reproductive success even when pollinators are scarce.
On the other hand, cross-pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different plant of the same species. Cross-pollination helps increase genetic diversity, which can result in healthier and more adaptable offspring.
Some plants have developed mechanisms to prevent self-pollination, such as having separate male and female flowers or having physical barriers between the male and female reproductive organs.
Overall, the different types of pollination contribute to the successful reproduction and fruit production in garden plants.
The Benefits of Pollination
Pollination plays a crucial role in ensuring the survival and genetic diversity of plant species. It is a natural process where pollen grains are transferred from the male part (anther) to the female part (stigma) of a flower, leading to fertilization and the production of seeds and fruits. The benefits of pollination are far-reaching and essential for fruit production in gardens.
- Increased fruit yield: Pollination ensures the transfer of pollen, facilitating fertilization, and resulting in the formation of fruits. Without pollination, many fruit-bearing plants would not be able to produce the fruits we enjoy.
- Genetic diversity: Pollination allows for the exchange of genetic material between different plants, leading to increased genetic diversity. This diversity is crucial for the adaptation and evolution of plant species, making them more resilient to environmental changes.
- Biodiversity support: Pollination is not only important for fruit production but also for maintaining biodiversity. It supports the reproduction and survival of many plant species, which in turn provide habitats and food for a wide range of animals and insects.
Pollination is vital for fruit production in gardens as it ensures increased fruit yield, genetic diversity, and supports overall biodiversity.
Factors Affecting Pollination
This paragraph will discuss the factors that can affect pollination, specifically weather conditions and the availability of pollinators.
Weather conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and wind, can greatly impact the success of pollination. Extreme temperatures or heavy rainfall can hinder the activity of pollinators and reduce the chances of successful pollination.
Additionally, the availability of pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and birds, is crucial for effective pollination as they are responsible for transferring pollen from one flower to another.
Therefore, understanding and managing these factors are vital for ensuring optimal fruit production in gardens.
Weather Conditions
Weather conditions play a crucial role in determining the success of fruit production in your garden.
Pollination, the transfer of pollen from the male reproductive part of a flower to the female reproductive part, is highly dependent on weather conditions.
Temperature, humidity, wind, and precipitation can all influence the behavior of pollinators and the viability of pollen.
For example, warm temperatures are favorable for the flight activity of bees and other pollinators, increasing the chances of successful pollination. However, extreme heat can also reduce pollen viability and affect the quality of fruit development.
Wind can disrupt the flight patterns of pollinators, while excessive humidity can cause pollen grains to become sticky and less likely to adhere to the stigma.
Additionally, rainfall during the flowering period can wash away pollen, reducing the chances of successful pollination.
Therefore, understanding and managing weather conditions is essential for ensuring optimal pollination and fruit production in your garden.
Availability of Pollinators
The presence of diverse and abundant pollinators is crucial for ensuring optimal fruit production and successful reproduction in a garden. Pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and birds, play a vital role in transferring pollen from the male reproductive organs of a flower to the female reproductive organs, enabling fertilization and subsequent fruit development.
The availability of pollinators in a garden is influenced by various factors, including the presence of suitable habitats and food sources. Providing a diverse range of flowering plants that bloom at different times throughout the growing season can attract and sustain a variety of pollinators. Additionally, minimizing the use of pesticides and creating sheltered areas, such as bee houses or butterfly gardens, can further enhance the availability of pollinators.
Ensuring a steady supply of pollinators in the garden is essential for maximizing fruit production and maintaining a healthy ecosystem.
How to Attract Pollinators to Your Garden
This discussion will focus on two important aspects of attracting pollinators to your garden: planting pollinator-friendly flowers and providing water and shelter for them.
Planting flowers that are known to attract pollinators, such as bee balm, lavender, and sunflowers, can help create a welcoming environment for these important insects.
Additionally, providing a water source and shelter, such as a bird bath or a bee hotel, can further enhance the attractiveness of your garden to pollinators.
Planting Pollinator-Friendly Flowers
Pollinator-friendly flowers play a crucial role in supporting fruit production in gardens as they attract and provide food sources for pollinators, ensuring effective pollination and subsequent fruit development. These flowers possess characteristics that specifically attract pollinators, such as vibrant colors, strong fragrances, and nectar-rich blooms.
Planting pollinator-friendly flowers in your garden can significantly enhance the presence of pollinators, leading to increased fruit yield. Some examples of pollinator-friendly flowers include:
- Sunflowers (Helianthus annuus): These flowers produce large, yellow blooms that attract a variety of pollinators, including bees and butterflies.
- Lavender (Lavandula spp.): Known for its aromatic fragrance, lavender flowers are highly attractive to bees, butterflies, and other pollinators.
- Coneflowers (Echinacea spp.): With their unique cone-shaped centers and colorful petals, coneflowers are excellent attractors for bees and butterflies.
- Marigolds (Tagetes spp.): Marigolds produce vibrant orange and yellow flowers that are irresistible to bees and butterflies.
By incorporating these pollinator-friendly flowers into your garden, you can create a welcoming environment for pollinators, ensuring successful fruit production.
Providing Water and Shelter for Pollinators
Water sources and sheltered areas are essential components for supporting and nurturing pollinators in a garden.
Pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds require water for hydration, especially during hot and dry weather conditions. Providing a water source can be as simple as placing a shallow dish filled with water and pebbles in the garden. This allows the pollinators to land on the pebbles and drink water without the risk of drowning.
Additionally, creating sheltered areas in the garden is crucial for pollinators to rest and seek protection from extreme weather conditions or predators. This can be achieved by planting dense shrubs or providing nesting boxes.
By ensuring the availability of water and shelter, gardeners can create a conducive environment for pollinators to thrive, thereby promoting successful fruit production.
Techniques for Hand Pollination
One effective method for hand pollination involves transferring pollen from the stamen of one flower to the stigma of another flower using a small brush or cotton swab. This technique is particularly useful in situations where natural pollinators are scarce or ineffective.
Hand pollination allows for controlled and targeted pollination, ensuring a higher success rate in fruit production. It is important to choose flowers that are ready for pollination, with open and receptive stigmas.
The process involves gently brushing the anthers of the donor flower to collect pollen, and then carefully transferring it to the stigma of the recipient flower. This method can be time-consuming, especially for plants with numerous flowers, but it can greatly enhance fruit set and yield, making it a valuable technique for gardeners and farmers.
Tips for Maximizing Fruit Production
Moving on from the techniques for hand pollination, it is crucial to consider various tips for maximizing fruit production in your garden. These tips aim to enhance the pollination process and create optimal conditions for fruit development.
Firstly, selecting the right plant varieties is essential, as some plants are self-pollinating while others require cross-pollination.
Additionally, providing a diverse range of flowering plants in your garden can attract a wide variety of pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and birds, ensuring efficient and thorough pollination.
Creating a suitable habitat for pollinators, such as offering nesting sites and avoiding the use of pesticides, is also crucial.
Furthermore, proper care and maintenance, including regular watering, pruning, and fertilizing, can contribute to healthy plant growth and fruit production.
By implementing these tips, gardeners can significantly increase the yield and quality of fruits in their gardens.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common pollinators found in gardens?
Some common pollinators found in gardens include bees, butterflies, moths, wasps, flies, beetles, and birds. These insects and animals play a vital role in transferring pollen between flowers, which is essential for fruit production in gardens.
Can fruit be produced without pollination?
Fruit cannot be produced without pollination as it is a crucial step in the reproductive process of plants. Pollination, achieved by transfer of pollen from male to female flower parts, leads to fertilization and subsequent fruit development.
How does weather affect the pollination process?
Weather conditions play a crucial role in the pollination process. Factors such as temperature, humidity, wind, and rainfall can affect the flight patterns and activity of pollinators, ultimately influencing their ability to transfer pollen between flowers and ensuring successful fruit production.
Are there any plants that self-pollinate?
Self-pollination occurs when plants transfer pollen from the anther to the stigma within the same flower or between flowers on the same plant. This process ensures reproductive success and can be found in various plant species.
What are some common reasons for poor fruit production in gardens?
Common reasons for poor fruit production in gardens include inadequate pollination, lack of proper pruning and fertilization, disease and pest infestations, unfavorable weather conditions, and improper watering and drainage.